Overview
An Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) clinic is a specialized medical facility dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment, and care of conditions related to the ear, nose, and throat. Whether it is restoring hearing, alleviating chronic sinusitis, or addressing sleep apnea, our ENT clinic is dedicated to improving patients' quality of life. Our ENT clinic is at the forefront of medical advancements, embracing innovative surgical techniques and treatments.
Treating a wide array of Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) conditions
If you have any specific questions or concerns about any ENT conditions or treatments, feel free to ask us for more information or assistance.
Otitis Media
Otitis Media is a common ear infection, often affecting children. It occurs when the middle ear becomes inflamed or infected. Symptoms may include ear pain, fever, and hearing difficulties. Treatment involves medication and pain management.
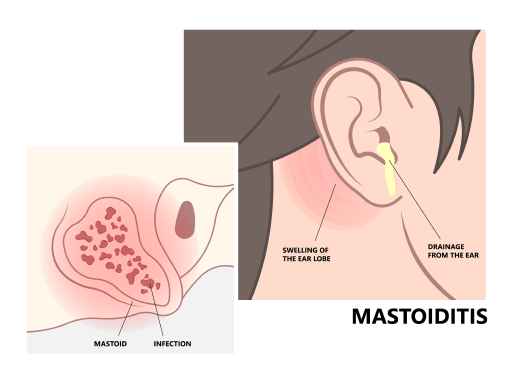
Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is a rare but serious infection of the mastoid bone, located behind the ear. It is caused by bacteria from an untreated middle ear infection. Symptoms include ear pain, fever, swelling behind the ear, and potential hearing loss. See a doctor right away if you have these symptoms.
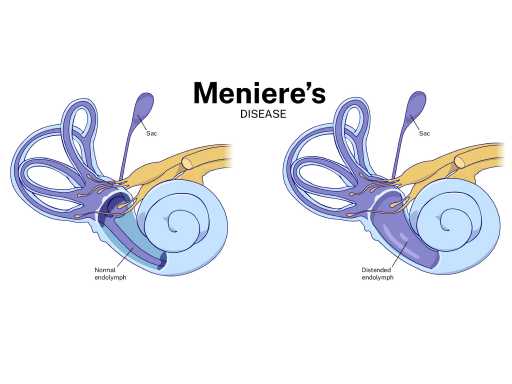
Meniere's disease
Meniere's disease constitutes a persistent inner ear condition marked by recurring episodes of vertigo (a sensation of spinning), frequently accompanied by tinnitus (ringing in the ear) and hearing impairment. The condition is attributed to an anomalous accumulation of fluid within the inner ear, resulting in equilibrium disturbances and auditory issues. Effective management encompasses dietary modifications, pharmaceutical treatments, and vestibular rehabilitation aimed at alleviating these symptoms.
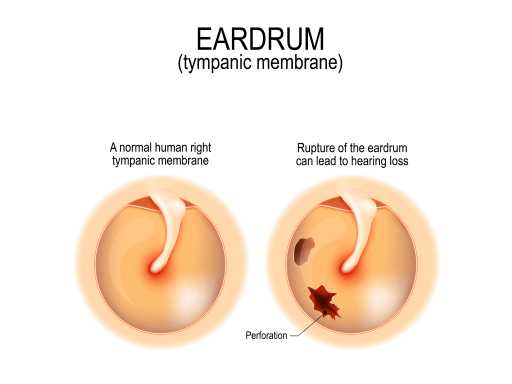
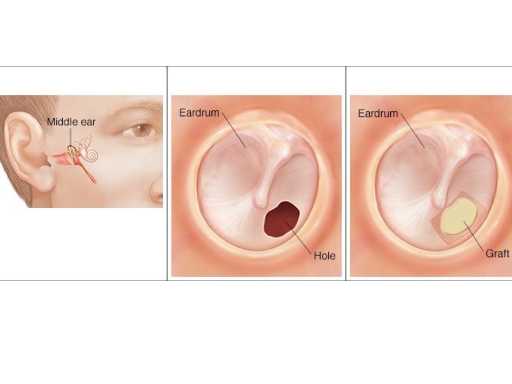
Perforated eardrum
A perforated eardrum refers to a tear or hole in the thin membrane that separates the ear canal from the middle ear. Common causes include ear infections, trauma, or sudden changes in pressure, such as from a loud noise or barotrauma during air travel. Symptoms may include ear pain, hearing loss, drainage from the ear, and increased susceptibility to infections. Treatment depends on the severity and include medication and rest. And in some cases surgical repair.
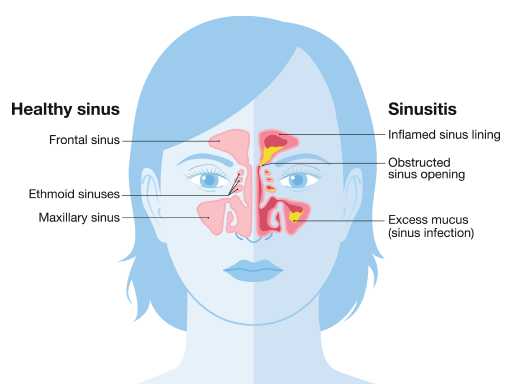
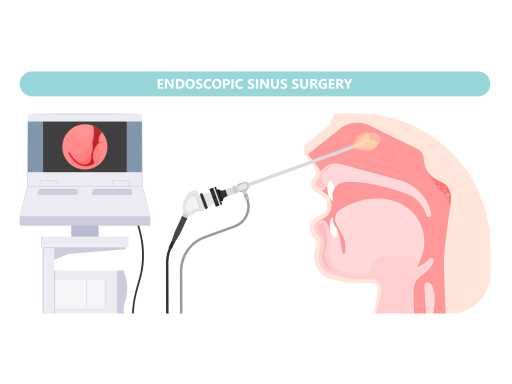
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is an inflammation or infection of the sinus cavities, often caused by viruses or bacteria. Common symptoms include facial pain, pressure, congestion, and a runny or stuffy nose. Acute sinusitis usually resolves with mild medication and rest, while chronic cases may require treatment with antibiotics and/or surgical management.
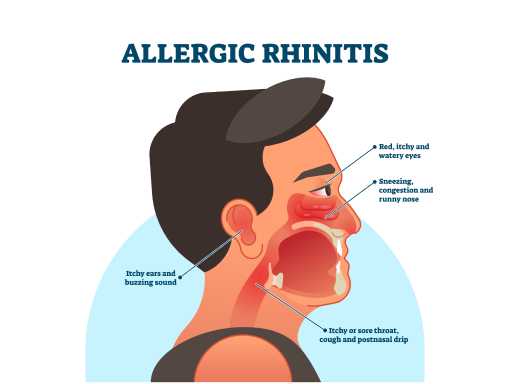
Allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis, commonly known as hay fever, is an allergic reaction to airborne allergens like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander. Symptoms include sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy or watery eyes, and often occur seasonally or year-round. Management includes allergen avoidance, antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, and allergy shots (immunotherapy) in severe cases. Diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve the quality of life for individuals affected by allergic rhinitis.
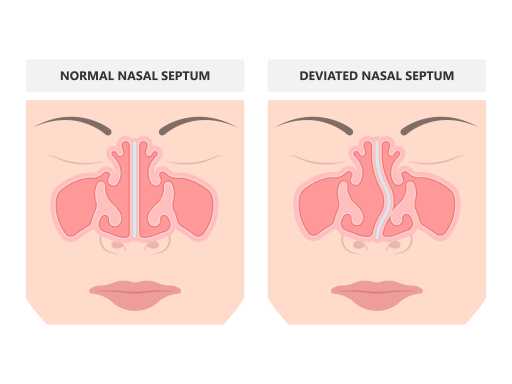
Deviated septum
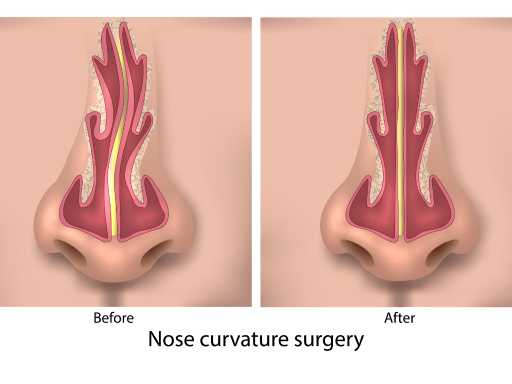
A deviated septum is a condition in which the thin wall (septum) inside the nose is displaced to one side. This deviation can obstruct airflow through one or both nostrils, leading to breathing difficulties. Common symptoms include congestion, snoring, frequent nosebleeds, and an increased risk of sinus infections. Surgical correction, known as septoplasty, is often recommended to improve nasal breathing in severe cases.
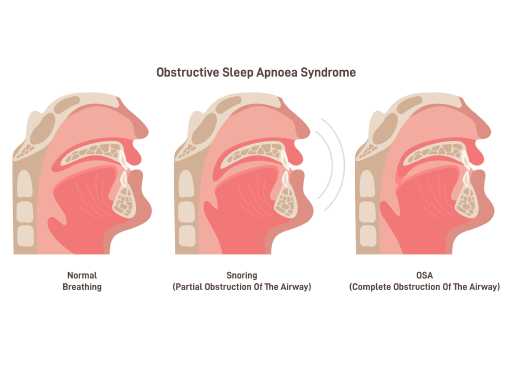
Sleep apnoea
Sleep apnoea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. These pauses, often caused by airway blockage, can lead to disrupted sleep and daytime fatigue. Common symptoms include loud snoring, gasping for air, and difficulty staying awake during the day. Effective treatments like continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy can significantly improve sleep quality and overall health.
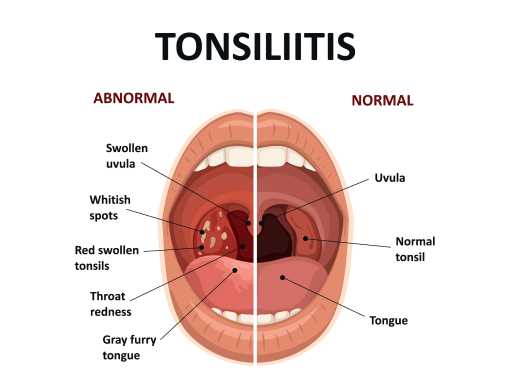
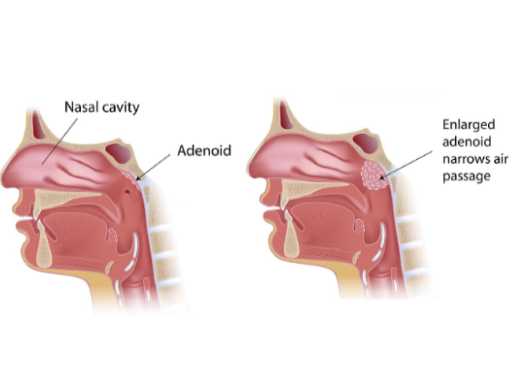
Tonsillitis
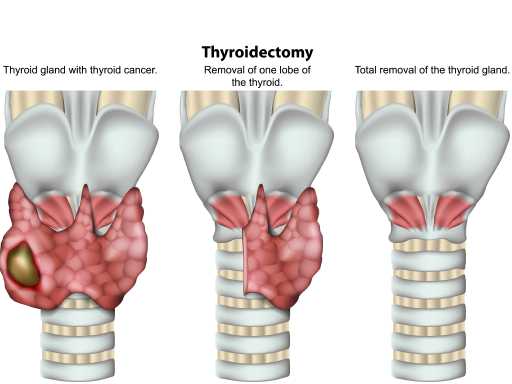
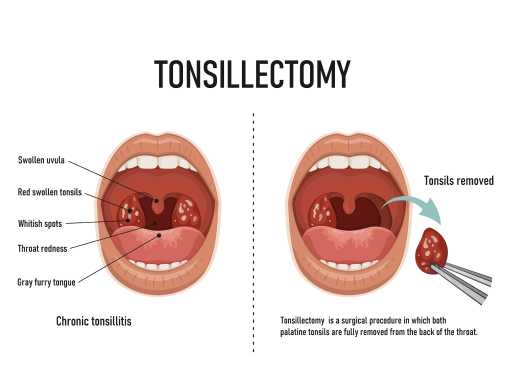
Tonsillitis is the inflammation of the tonsils, which are located at the back of the throat. It is usually caused by a viral or bacterial infection and can lead to symptoms like sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and fever. Treatment depends on the cause, with viral cases managed with rest and pain relief, while bacterial infections may require antibiotics. In severe or recurrent cases, the doctor may recommend tonsillectomy, the surgical removal of the tonsils.
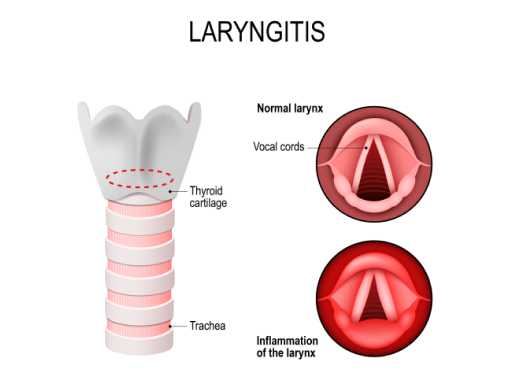
Laryngitis
Laryngitis is the inflammation of the larynx, often resulting in a hoarse or lost voice. It is caused by viral infections, overuse of the voice, or irritation due to smoking or allergies. Resting the voice, staying hydrated, and avoiding irritants can help with recovery. In many cases, laryngitis requires medical attention, especially if it persists for an extended period.

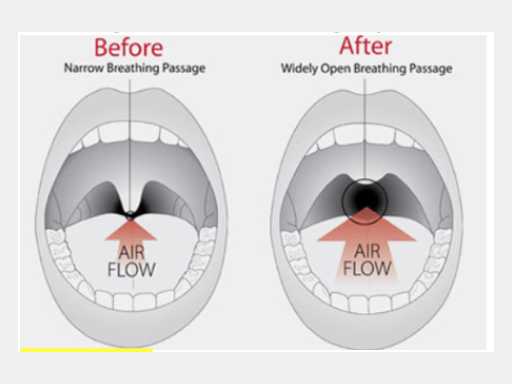
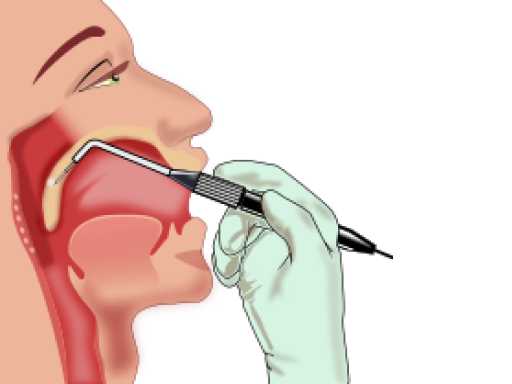
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): This procedure removes excess tissue from the back of the throat, including the uvula, soft palate, and tonsils.
Maxillomandibular advancement (MMA): This procedure moves the upper and lower jaws forward to widen the airway.
Genioglossus advancement (GA): This procedure moves the tongue forward to enlarge the airway.
Tracheostomy: This procedure creates a hole in the neck and inserts a tube into the trachea (windpipe) to bypass the upper airway.
Preventing and managing vertigo or balance disorders can involve several strategies
Prevention:
Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can contribute to dizziness, so ensure you drink enough water.
Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can improve balance and reduce the risk of falls.
Manage Stress: Stress and anxiety can worsen vertigo, so stress reduction techniques like meditation or deep breathing may help.
Medication Review: Some medications can affect balance; consult your doctor to evaluate if any medications are contributing to your symptoms.
Management:
Vestibular Rehabilitation: A specialised physical therapy program can improve balance and reduce vertigo symptoms.
Canalith Repositioning Procedures: Techniques like the Epley maneuver can reposition displaced inner ear crystals causing benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.
Medications: Depending on the underlying cause, medications like anti-nausea drugs, vestibular suppressants, or antibiotics for infections may be prescribed.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Modify daily activities to minimise the risk of falls, such as using handrails, avoiding rapid head movements, or using walking aids if necessary.
Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be considered for severe, persistent, or structural issues causing vertigo.
It is essential to consult an ear, nose, and throat specialist for a thorough evaluation and personalised treatment plan if you experience persistent vertigo or balance problems.
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of sleep apnoea, individual patient factors, and the underlying causes. It is essential to consult with a sleep specialist who can assess your condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment option. Surgery is primarily reserved for cases where non-surgical treatments have not been successful or when there are structural issues that can be corrected surgically. Non-surgical options of managing sleep apnoea include:
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy: This is the most common and effective non-surgical treatment. A CPAP machine delivers a steady stream of air through a mask to keep the airway open during sleep.
Bi-level Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) Therapy: Similar to CPAP but with variable pressure settings for inhaling and exhaling, which can be more comfortable for some patients.
Oral Appliances: Dentists can provide custom-made oral devices that reposition the jaw and tongue to keep the airway open, particularly effective for mild to moderate sleep apnoea.
Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss, positional therapy (sleeping in certain positions), avoiding alcohol and sedatives, and managing allergies or nasal congestion can help improve symptoms in some cases.
Inspire Therapy: A surgically implanted device that stimulates the hypoglossal nerve to prevent airway collapse during sleep, suitable for specific cases of obstructive sleep apnoea.
Yes, earwax buildup is a common issue. It can be safely removed by an ear specialist using methods like irrigation or manual removal with specialised instruments. It is important to avoid inserting objects into the ear, as this can push wax deeper or cause injury.
Chronic sinusitis is caused by persistent inflammation of the sinus passages, often resulting from various factors:
Infections: Recurrent or untreated acute sinus infections can lead to chronic inflammation.
Allergies: Allergic reactions to pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or other allergens can trigger chronic sinusitis.
Nasal Polyps: Benign growths in the nasal passages can obstruct the sinuses and contribute to chronic inflammation.
Deviated Septum: A crooked or deviated nasal septum can obstruct airflow, making sinusitis more likely.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to irritants like smoke or pollution can exacerbate sinusitis symptoms.
Treatment options depend on the type and severity of hearing loss and may include hearing aids, cochlear implants, and speech therapy. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for the best outcomes in children with hearing loss.
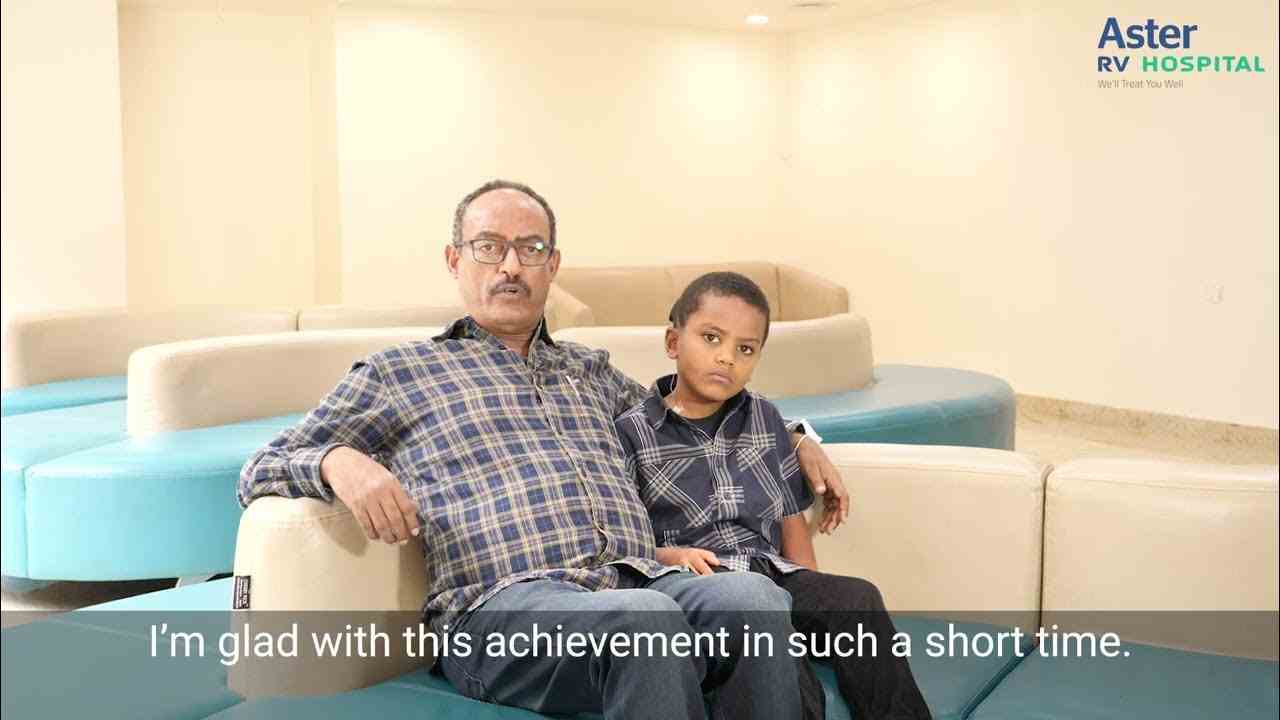
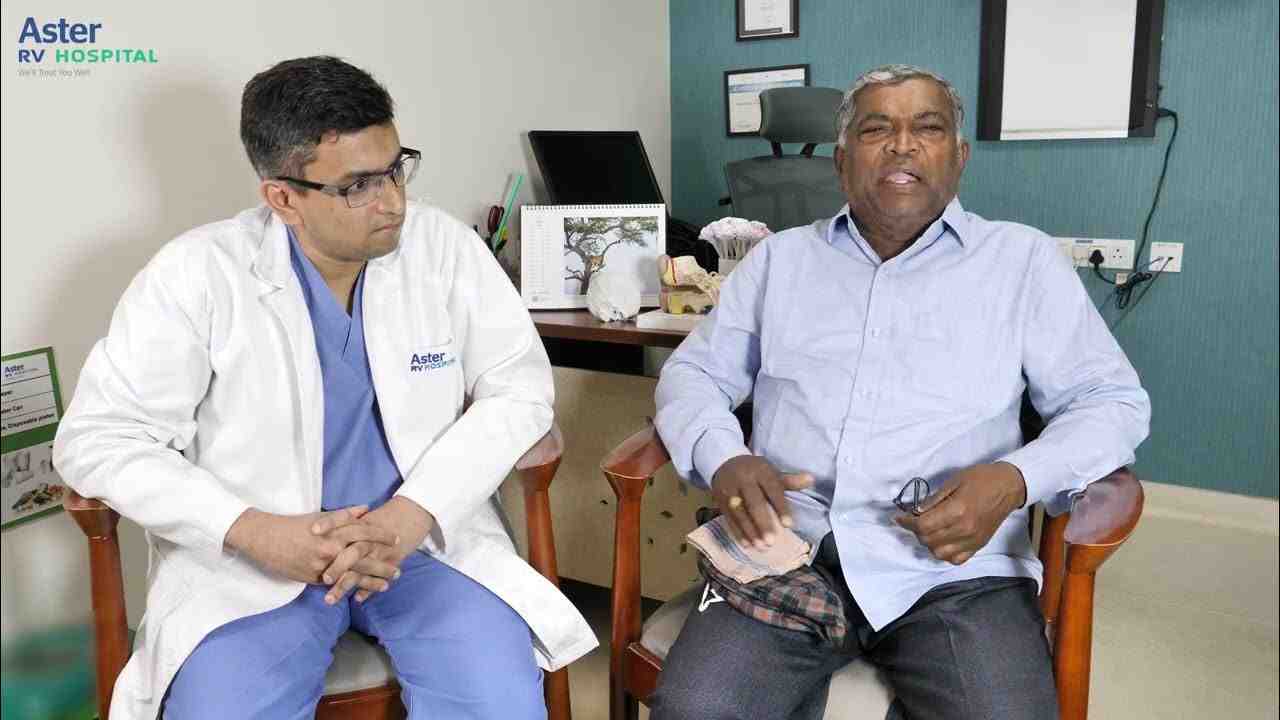
Let's hear from our Patient's