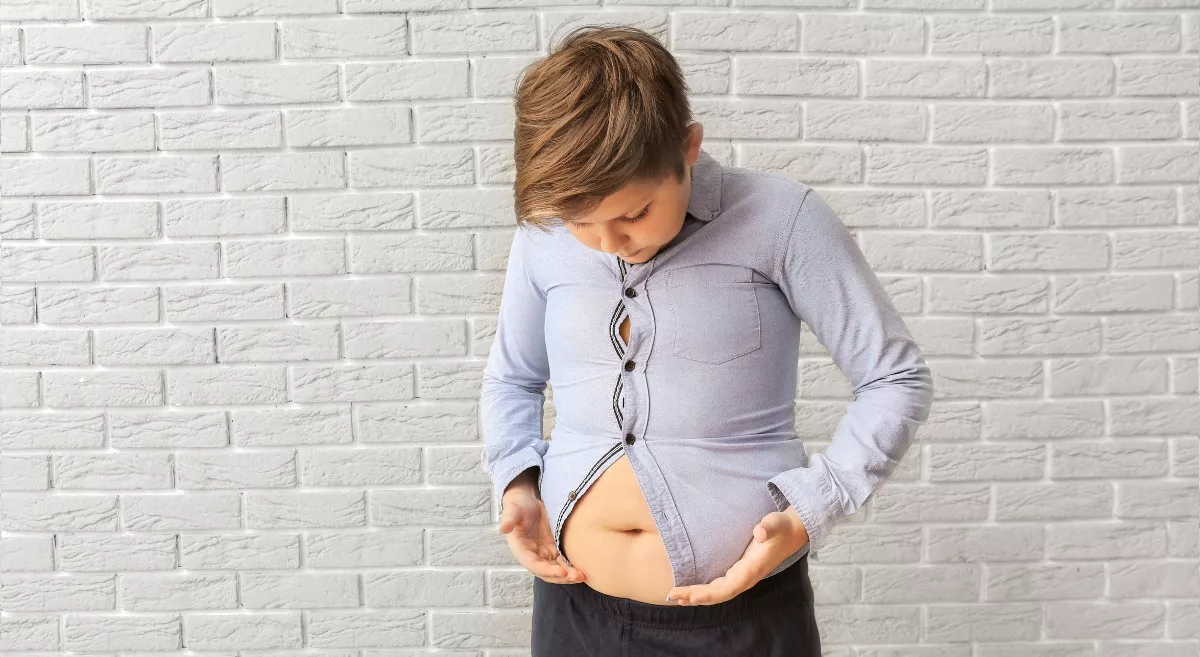
With our current lifestyle, obesity and hormonal issues are very common among adolescents, causing significant health risks and impacting their overall well-being. Adolescence is a critical period for growth and development, during which hormones play a crucial role in shaping both physical and emotional health. Addressing these intertwined issues requires a proper understanding of the factors that play a role and how to effectively manage them at individual, family, and community levels.
What Causes Obesity in Adolescents?
Obesity in adolescents is typically defined by a body mass index (BMI) at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex. Several factors contribute to the rise in obesity rates among young people, including:
- Dietary Habits: Increased consumption of high-calorie, low-nutrient foods, sugary beverages, and snacks contributes to excess weight gain. Busy lifestyles often lead to reliance on fast food and processed snacks, which are convenient but unhealthy.
- Physical Inactivity: Sedentary behaviors, such as excessive screen time and lack of physical activity, are major contributors to obesity. Many adolescents engage less in sports and outdoor activities, leading to a decrease in energy expenditure.
- Psychosocial Factors: Emotional challenges, including stress, anxiety, and depression, can lead to unhealthy eating behaviors. Adolescents may use food as a coping mechanism, resulting in weight gain.
- Genetics and Environment: Genetic predisposition can influence body weight, but environmental factors, such as family habits, cultural norms, and socioeconomic status, also play a significant role.
Hormonal Imbalances in Adolescents
Body weight or body composition could be affected by hormonal influences during growth and development. Insulin, leptin, and ghrelin are the main hormones that control hunger, feeling full, or even how much fat the body can accumulate. Hormonal imbalance can be caused in adolescents due to obesity, leading to these further complications:
- Insulin Resistance: People with an extreme amount of body fat create more cells that become insulin-insensitive. When this happens, it causes an increase in blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Leptin Resistance: Leptin is a hormone that helps regulate energy balance by inhibiting hunger. When obesity is present, it may even appear that more leptin is needed, often resulting in what’s seen as an insatiable appetite while also decreasing energy outputs.
- Hormonal Changes: The same holds for females; however, this most usually occurs with females who suffer from polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which leads to abnormal menstrual cycles, acne, and increased fat deposition, while in males, depressive feelings and other such symptoms appear.
How to Manage Obesity and Hormonal Issues in Adolescents?
Effectively managing obesity and hormonal issues in adolescents requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Encouraging Healthy Eating Habits
- Balanced Diet: Ensure that your child eats a balanced diet which includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean protein. Teach them about portion size, healthy and unhealthy food choices, and nutritional value.
- Limit Soda and High-Calorie Snacks: Lower the intake of sugary drinks and other forms of high-calorie and unhealthy snacks. As a substitute, promote milk, water, and fresh fruit to the adolescent population.
- Involvement in the Meal Planning and Preparation Stage: Encourage adolescents to plan and help prepare food. This teaches them useful skills and helps them take responsibility over their food consumption.
- Increasing Physical Activity
- Exercise on a Regular Basis: Aim for moderate to vigorous exercise for 60 minutes every single day. Sports, dancing, biking, or simply walking can all be considered as activities. Such enjoyable forms of exercise are likely to appeal to the youth.
- Screen Time Reduction: You can also try restricting television, video games, and other forms of social media that require one to be seated. Instead, entice them with outdoor activities and family gatherings encouraging movement.
- Addressing Emotional Health
- Create a Supportive Environment: Encourage discussions and openness about feelings, struggles with food, and eating at home. Don’t underestimate the emotional side of food and eating, and educate on how to cope with food cravings and other issues.
- Seek Professional Help When Necessary: If required, seek the help of mental health professionals who specialize in adolescent health. Therapy can address underlying issues such as depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem that may contribute to obesity.
- Monitoring and Medical Intervention
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular visits to healthcare providers, including Gastroenterology Hospital in Hebbal Bangalore, are essential for monitoring growth, weight, and hormonal health. Healthcare providers can offer tailored advice and interventions based on individual needs.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage obesity or hormonal issues. This should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Hormonal Treatments: For adolescents with hormonal imbalances like PCOS, appropriate hormonal treatments can help manage symptoms and regulate menstrual cycles.
- Family Involvement and Education
- Family-Based Programs: Involving the entire family in lifestyle changes can foster a supportive environment and enhance the chances of success. Family-based interventions have been shown to be effective in managing obesity in adolescents.
- Education and Resources: Provide educational resources to families about nutrition, physical activity, and the importance of mental health. Community programs and workshops can help families implement healthier lifestyles.
- Support and Resources Available in the Community
- Community Programs: Leverage the services of national or local organizations, such as public health agencies, schools, or community organizations that offer programs aimed at supporting healthy lifestyles. Most communities have sports, physical activity, as well as life skills training programs for young teenagers.
- Policy Advocacy: Policies such as comprehensive nutrition policies for children and more opportunities for physical activities during school should be promoted. Additionally, consulting with experienced Gastroenterologists in Hebbal Bangalore can provide expert guidance on digestive health as part of overall adolescent wellness.
Conclusion
It is possible to treat obesity and hormonal difficulty disorder in adolescents, but assisting them should always be holistic in nature. Someone will help them formulate a diet plan, encourage them to exercise, and even work with the child or teen’s emotions, and whole families and entire communities have to be involved to make this all effective. Information and prevention will allow adolescents to effectively use this difficult development stage without negative effects, and being physically and mentally supported. As health providers, families, and communities of youth combine efforts, it is possible to prevent adolescent obesity and hormonal disorders and expect a better health outcome in the future.