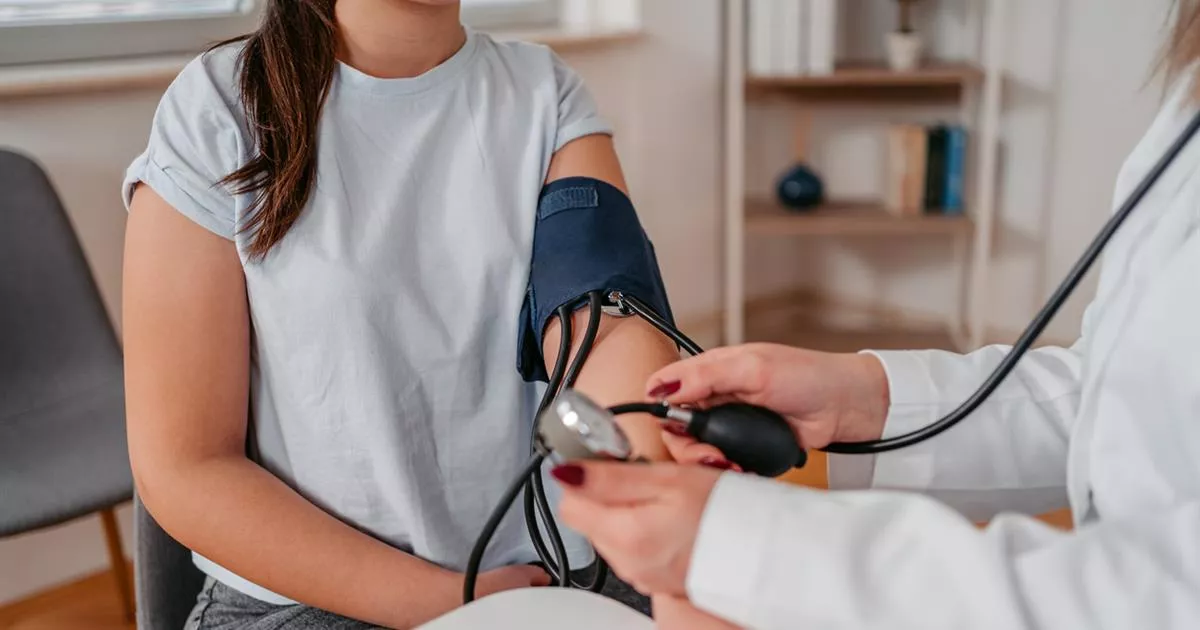
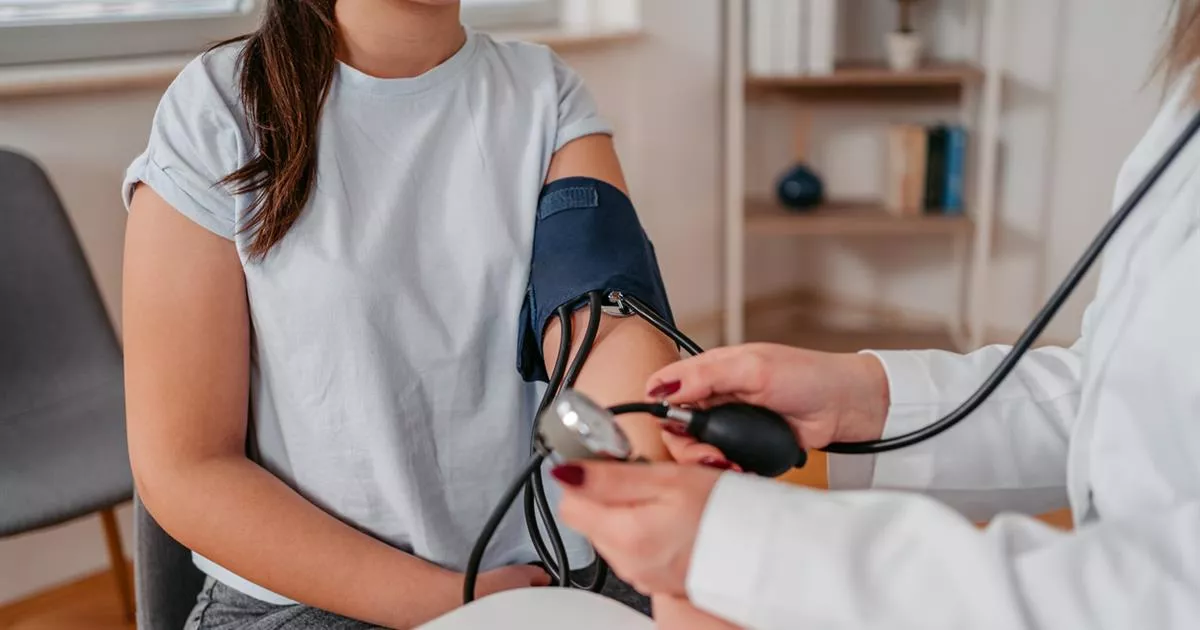
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While most cases of hypertension can be effectively managed with lifestyle changes and medications, there is a subset of patients who experience resistant hypertension. Resistant hypertension refers to blood pressure that remains high despite the use of three or more antihypertensive medications. In such cases, careful medication management becomes crucial to achieve optimal blood pressure control. Patients in Kerala often consult a cardiologist in Kochi Kerala to better understand and manage such complex hypertension cases. In this blog post, we will explore the essentials of medication management in resistant hypertension.
- Accurate Diagnosis: The first step in managing resistant hypertension is to ensure an accurate diagnosis. This involves ruling out any underlying medical conditions that may contribute to high blood pressure, such as kidney disease, hormonal disorders, or obstructive sleep apnea. Identifying and addressing these underlying causes can help improve blood pressure control, and visiting a reputed cardiology hospital in Kochi Kerala can support thorough evaluation and testing.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Alongside medication, lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in managing hypertension. Patients with resistant hypertension should focus on adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, limited sodium intake, and moderation in alcohol consumption. These lifestyle changes can help lower blood pressure and enhance the effectiveness of medications.
- Medication Review: It is crucial to review the patient's current medication regimen to identify any potential factors contributing to resistant hypertension. Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and oral contraceptives, can interfere with blood pressure control. Assessing the appropriateness of the current medications and making necessary adjustments can significantly impact treatment outcomes.
Combination Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While most cases of hypertension can be effectively managed with lifestyle changes and medications, there is a subset of patients who experience resistant hypertension. Resistant hypertension refers to blood pressure that remains high despite the use of three or more antihypertensive medications. In such cases, careful medication management becomes crucial to achieve optimal blood pressure control. In this blog post, we will explore the essentials of medication management in resistant hypertension.
- Accurate Diagnosis: The first step in managing resistant hypertension is to ensure an accurate diagnosis. This involves ruling out any underlying medical conditions that may contribute to high blood pressure, such as kidney disease, hormonal disorders, or obstructive sleep apnea. Identifying and addressing these underlying causes can help improve blood pressure control.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Alongside medication, lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in managing hypertension. Patients with resistant hypertension should focus on adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, limited sodium intake, and moderation in alcohol consumption. These lifestyle changes can help lower blood pressure and enhance the effectiveness of medications.
- Medication Review: It is crucial to review the patient's current medication regimen to identify any potential factors contributing to resistant hypertension. Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and oral contraceptives, can interfere with blood pressure control. Assessing the appropriateness of the current medications and making necessary adjustments can significantly impact treatment outcomes.
- Combination Therapy: Resistant hypertension often requires a combination of different classes of antihypertensive medications to effectively lower blood pressure. Combining medications with different mechanisms of action, such as diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), and calcium channel blockers, can provide synergistic effects and improve blood pressure control.
- Adherence and Compliance: Medication adherence is critical in the management of resistant hypertension. Patients must understand the importance of taking their medications as prescribed and adhere to the recommended dosing schedule. Healthcare providers should educate patients about potential side effects, discuss strategies to minimize them, and provide support to enhance compliance.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular monitoring and follow-up are essential in managing resistant hypertension. Blood pressure should be closely monitored, and adjustments to the medication regimen should be made based on the patient's response. Additionally, healthcare providers should assess for any adverse effects, evaluate the patient's overall cardiovascular risk, and address any underlying conditions that may be contributing to resistant hypertension.
- Specialist Consultation: In some cases, resistant hypertension may require the expertise of a specialist, such as a nephrologist or a hypertension specialist. These healthcare professionals have in-depth knowledge and experience in managing complex cases of hypertension. Consulting a specialist can provide valuable insights and help optimize treatment strategies for patients with resistant hypertension.
In conclusion, medication management in resistant hypertension requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond simply increasing the dosage of antihypertensive medications. Accurate diagnosis, lifestyle modifications, medication review, combination therapy, adherence, monitoring, and specialist consultation are all crucial components of an effective management plan. By addressing these aspects, healthcare providers can work together with patients to achieve optimal blood pressure control and reduce the risks associated with resistant hypertension. Remember, managing hypertension is a journey that requires patience, commitment, and collaboration between patients and healthcare professionals.