The gallbladder is a small organ that is located just under the liver. It stores and periodically releases bile, a digestive fluid. Bile is produced in the liver and released into the small intestine. It helps in the digestion of food.
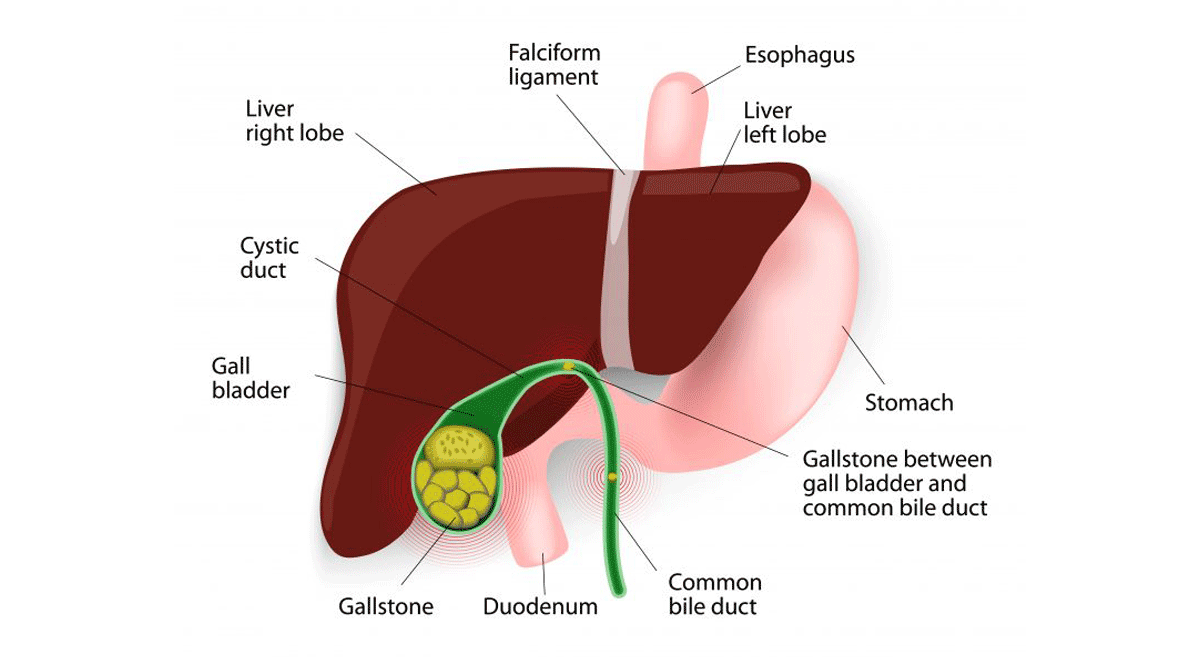
Gallbladder stones, commonly referred to as gall stones or cholelithiasis, are small hardened deposits of cholesterol and bilirubin that form in the gall bladder. Bilirubin is a substance produced by the body when the red blood cells or RBCs start to break down.
Gallbladder stones may be small or grow to the size of a golf ball. As they grow in size, gallbladder stones can block the bile duct, causing pain. This condition requires medical attention and treatment. Aster Whitefield Hospital in Banglore is one of the top hospitals in India for gallbladder stone surgery.
Difference Between Gall Bladder and Urinary Bladder
The gall bladder is a small organ located under the liver. It stores and releases bile, which helps the body break down fats and absorb certain nutrients. The urinary bladder is a sac-like organ located in the lower part of the abdomen. It stores urine until it is released from the body through urination.
Symptoms of gallbladder stones
Gallbladder stones may be small, like grains of sand. At this stage, there may be no symptoms or discomfort. Many people with small gallstones do not know they are there and require no treatment. When they are large, more in number, and start to obstruct the bile duct, they may cause some of the following symptoms -
- Discomfort or pain in the right upper abdomen
- Pain radiating to the right shoulder or the back
- Nausea or vomiting
- Heartburn, gas, indigestion
- Frequent digestion issues
- Yellow skin or eyes
- Dark urine
- Fevers and chills.
Misconceptions about Gallbladder stones
Gallstones are among the most misunderstood disorders. It is estimated that many people live with gallstones without experiencing any significant symptoms. In some cases, gallstones may cause infections, severe pains, or disorders like pancreatitis. There are several misconceptions about the condition and its treatment. It is best to discuss your symptoms with doctors from Aster Whitefield hospital to get an accurate diagnosis and a personalised treatment plan.
Busting Myths
Myth 1. Gallbladder flush
Fact - One of the common home remedies that are recommended for gall stones is drinking mix of olive oil, herbs and apple cider vineger.There is no scientific research indicating that milk consumption can reduce or treat gallbladder stones. It is essential to follow the treatment for gallbladder stones as recommended by a doctor at Aster whitefield hospital.
Myth 2. Drinking more Apple Juice
Apple juice or apple cider vinegar is often said to treat gallstones without gallbladder removal surgery. This is also a myth. There is no scientific proof to support such a theory. Gallstones may or may not require surgery. The recommendation or treatment plan should come from an experienced doctor.
Myth 3. Dandelion
Historically it was believed that dandelion tea will increase the bile flow and will flush out gall stones. No scientific data will support this theory.
Myth 4. Removing the gallbladder is the ultimate solution
While it is true that in some instances, gallbladder removal is a recommended part of your treatment plan, surgery is not always necessary. If the gallstones are small and cause no symptoms, your doctor at Aster Whitefield hospital may recommend medication and monitoring.
Myth 5. Stone will pass through the urine
Unlike kidney stones, gallbladder stones will not pass through the urine. Consumption of water and staying hydrated will not remove the fatty substances in your food and will not prevent gallstones from forming. To understand more about the recommended course of treatment for gallbladder stones, talk to your doctor.
Preventing Gallbladder stones
Scientists and researchers are still not clear if gallbladder stones can be prevented. However, there are certain changes you can make to your diet and lifestyle to reduce the risk of developing gallstones.
Maintain a healthy weight
Obesity increases the risk of developing gallstones. Maintaining a healthy weight through dietary changes and exercises will reduce the chances of developing gallstones.
Consume a balanced diet
Adding fish, and limiting the intake of fatty foods are believed to reduce the risk of developing gallstones. Add more whole grains to your diet. Adding low-fat dairy products and fresh vegetables and fruits will help maintain a good diet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are gallbladder stones serious?
In some cases, gallstones do not cause any severe symptoms. You may not even know you have gallstones unless there is an incidental finding. However, gallbladder stones may obstruct the bile duct and may even cause pancreatitis in some cases. An infection may accompany this condition. These cases are severe and need gallbladder stone treatment or gallbladder removal surgery.
What is the main cause of gallstones?
Gallstones are formed if bile contains excess cholesterol or excess bilirubin. The bile may contain a lower quantity of bile salts in these cases. The exact cause for the formation of gallstones is not fully clear to scientists.
What happens if gallstones are left untreated?
If your gallstones are minor and do not cause any symptoms, doctors may recommend regular monitoring without treatment or recommend some medicine for gallstones. Surgery is recommended if the gallstone is big or obstructive. If the doctor suspects that the gallstone is growing and may soon cause discomfort, they may recommend surgery. In these cases, you should not let the gallstones remain untreated.
What should I avoid eating with gallstones?
If you have developed gallstones, it is recommended that you avoid rich, oily foods. Whole fat milk and packaged foods are best avoided as well. Speak to your doctor at Aster Whitefield hospital about recommended dietary changes.