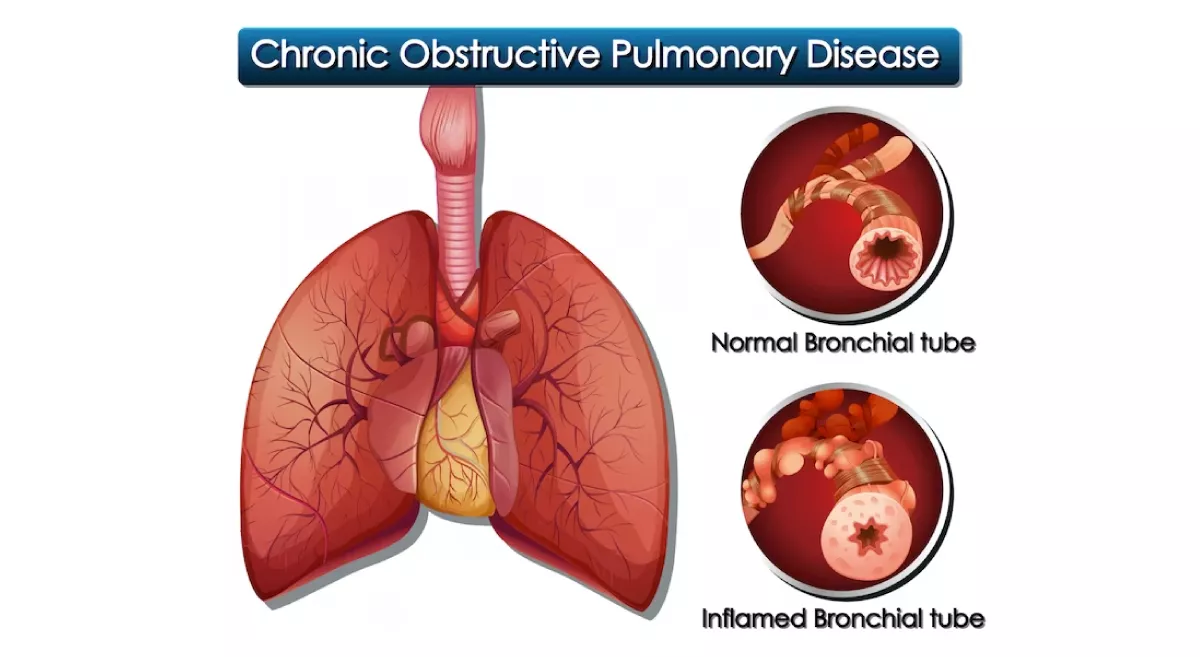
What is COPD ?
COPD stands for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. It is a chronic lung disease that makes it difficult to breathe. COPD is a progressive disease, meaning it gets worse over time.The main cause of COPD is smoking, but long-term exposure to air pollution, second-hand smoke, and other irritants can also contribute to the disease. COPD is most common in people over the age of 40 and is more common in men than women. The two main forms of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. In chronic bronchitis, the airways become inflamed and narrowed, which leads to coughing, phlegm production, and shortness of breath. In emphysema, the air sacs in the lungs become damaged, which makes it difficult to breathe. Early evaluation by experienced Pulmonologists In JP Nagar Bangalore can help in timely diagnosis and better disease management.
Symptoms of COPD :
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Wheezing
- Chronic cough, with or without mucus
- Chest tightness
- Fatigue
- Recurrent respiratory infections
COPD is diagnosed with a combination of medical history, physical exam, lung function tests, and imaging tests. Although there is no cure for COPD, various treatments exist that can assist in symptom management and decelerating the advancement of the disease. Treatment options may include medications to open the airways and reduce inflammation, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and avoiding air pollutants. In severe cases, surgery or lung transplantation may be considered, often under the guidance of a specialized Pulmonology Hospital in JP Nagar Bangalore.
How is COPD managed ?
The medical management of COPD includes several treatment options that can help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. Here are some of the most common medical management strategies for COPD:
Bronchodilators:
These are medications that help relax the muscles around the airways, making it easier to breathe. Bronchodilators can be short-acting or long-acting and may be delivered through an inhaler or a nebulizer.
Corticosteroids:
Inhaled corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation in the airways and may be used in combination with bronchodilators.
Oxygen therapy:
This may be used to provide supplemental oxygen to people with severe COPD who have low levels of oxygen in their blood.
Pulmonary rehabilitation:
This is a program that includes exercise, breathing techniques, and education to help improve lung function and quality of life.
Flu and pneumonia vaccines:
These can help prevent respiratory infections, which can exacerbate COPD.
Antibiotics:
Antibiotics may be used to treat bacterial infections that can cause COPD exacerbations.
Lung volume reduction surgery:
This is a surgical procedure that removes damaged lung tissue to improve lung function.
Lung transplant:
Consideration may be given to a lung transplant in severe cases.
In addition to these medical treatments, lifestyle changes can also help manage COPD symptoms. These may include quitting smoking, avoiding air pollutants, eating a healthy diet, staying physically active, and avoiding respiratory infections. People with COPD should work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan based on their individual needs and symptoms.